What is reverse osmosis
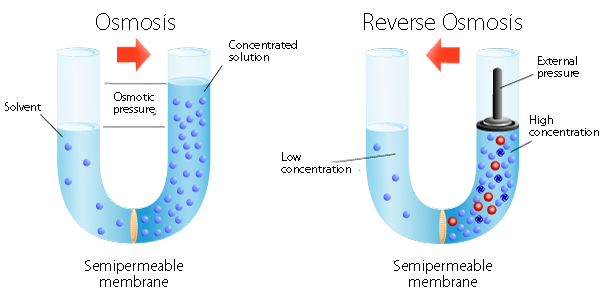
To better understand Reverse Osmosis let’s first discuss Osmosis. In both botany and chemistry, Osmosis, is the flow of one constituent of a solution through a membrane while the other constituents are blocked and unable to pass through the membrane.
A membrane, in biology, is any thin layer of connective tissue coating individual cells and organs of the body, or lining the joints and the ducts and tracts that open to the exterior of the body. A constituent is an essential part of a solution. The hydrostatic pressure needed to allow fluids to pass through a membrane is called osmotic pressure.
An example of a membrane would be the thin, clear tissue that is found separating an eggshell, and the white of an egg. Pure water that has fewer dissolved substances can pass through this type of semi permeable membrane, but water that has a greater number of constituents, will flow slower or not at all.
Reverse osmosis process
In reverse osmosis, the desalination of water is a membrane separation process in which the water from a pressurised saline solution is separated from the solutes and flows through an appropriate membrane. The permeate (the water flowing through the product tube of the membrane), which generally emerges near atmospheric pressure, is reduced in salt content while the feed solution which is pressurised on the other side of the membrane increases in salt content.
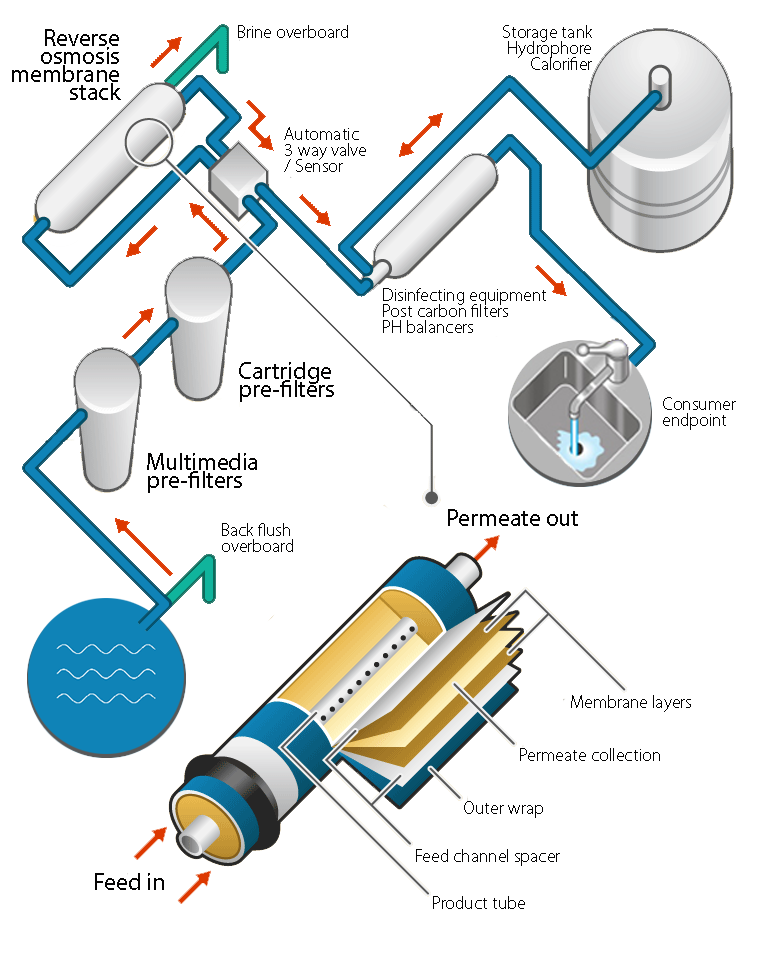
What makes an RO watermaker:
Supply pump
which supplies the feed water necessary for the high-pressure pump to operate. A sufficient supply pump with good suction head properties is required for proper function and longevity.
High pressure pump
is a crucial component for building pressure essential to creating the reverse osmosis phenomena.
Filtration
is the next and the most important part of any water-making unit. This is done in various ways and stages. The most common pre-filtration is the use of media filtration, using several different types of media (for removal of larger particles, 30 microns). In comparison, the diameter of a cross section of a human hair is 84 microns. Cartridge filters remove particles down to 5 microns in size
Pressure vessels
houses the heart of the reverse osmosis operation; the membranes of a water maker.

Membranes are layers sandwiched together and spirally wound over a perforated plastic tube (product tube). The layers are then covered with a layer of fiberglass. The actual membrane is a thin porous film between two mesh-like layers, serving as a spacer for the water to flow over it.
There are different types of membranes for different purposes. The three basic types are; freshwater, brackish, and seawater; each designed for a specific rate of particle rejection. The permeate passes through sensors detecting its flow and quality.
It is important to note that the polyamide membrane material is intolerant of oxidizers such as chlorine. Any interaction to chlorine or other oxidizers will result in permanent damages.
|
More information
|
 |
|
|
|
Address
Industmarine Engineers
32 Toh Guan Road East
#01-09 Enterprise Hub
Singapore 608578
32 Toh Guan Road East
#01-09 Enterprise Hub
Singapore 608578
Contact No : 6774 6220
Email : enquiry@industmarine.com
About Us
Industmarine Engineers’ continual distinction in embodying our core philosophies of innovation, the human touch and active engagement has helped establish our company as a regional leader for providing products and services pertaining to the marine industry.
Read More
Read More
© 2017 Industmarine | All Rights Reserved

